
The shift to direct-to-consumer (D2C) sales in the automotive industry has been significant in recent years. Technology and consumer preferences have changed car sales models, which used to be done at dealerships. The automotive retail industry is changing drastically. Technology, consumer preferences, and the COVID-19 pandemic are driving online and DTC car sales. This article discusses these trends, their drivers, and their effects on automotive retail.
Dealerships have traditionally dominated automotive retail. Before buying, consumers visited showrooms, spoke to salespeople, and drove cars. Car buying habits have changed over time. Online automotive retail began with basic information and price comparisons, laying the groundwork for modern digital platforms.
The Rise of Online Sales
Several factors are driving online auto sales. Technological advances have enabled seamless, user-friendly car-buying e-commerce platforms. The COVID-19 pandemic reduced physical interactions and pushed more transactions online, changing consumer preferences for online shopping.
Online automotive retailers include established automakers and new market entrants. Tesla pioneered direct sales, bypassing dealerships. Online-only retailers like Carvana have also made significant gains by offering a fully digital car buying experience.
The benefits of online auto sales are significant. Shopping from home and comparing vehicles online save consumers time. Due to their wider reach, automakers can collect data for personalized marketing strategies on online sales platforms.
Understanding the Dealers' Point of View

Mercedes-Benz and Volkswagen, among other OEMs, have adopted an automotive direct-sales model for some markets and product lines in recent years. Customers can buy new cars from dealerships or OEMs online. Negotiations with dealers are no longer allowed, so the manufacturer-set retail price (MSRP) applies everywhere.
Direct-to-consumer sales allow OEMs to charge higher prices because dealerships must follow the MSRP and cannot undercut each other. Online sales are cheaper than dealership sales. OEMs can now capture, own, and use customer relationship-building data thanks to digital technologies.
Automotive Direct-Sales Receives Mixed Reviews
Nearly 60% of the 400 dealers we spoke with have not adopted an agency model, and 80% of conventional dealers think it would hurt their business.
According to 75%, OEMs have not provided enough detail on the new model, roles, and transition period. For 66%, agency compensation is unfair, and pricing is unlikely to be demand-oriented and dynamic.
Conventional dealers also questioned the pricing and commission changes. Many find that used and demo cars, after-sales service, and financing are more profitable than new car sales, which are just a way to get customers into the dealership for servicing. Dealers fear the agency model could ruin their business because they don't know how the automotive direct-sales model will affect their bottom line.
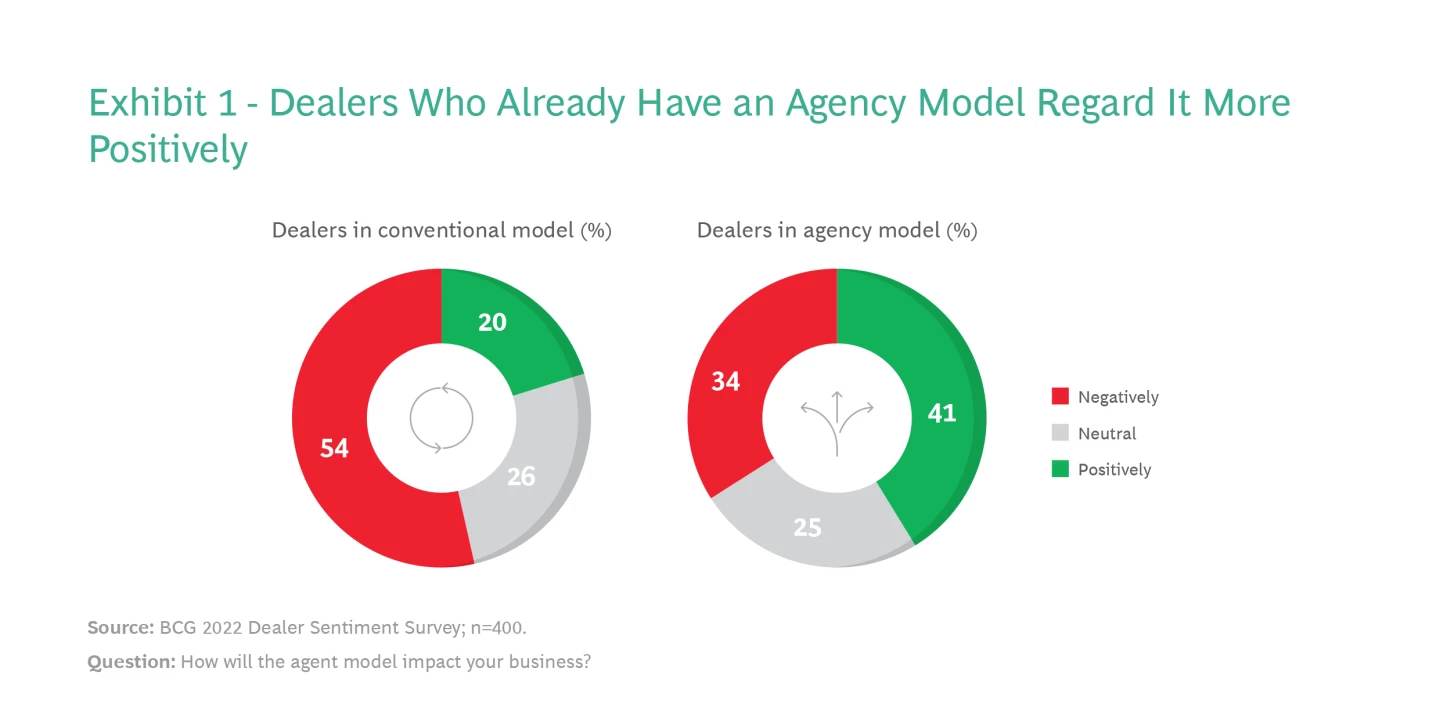
Dealers who use the agency model seem to like it. See Exhibit 1. More than half of conventional dealers dislike it, compared to one-third of early adopters. Conventional dealers like the agency model 20%, while early adopters like it twice as much. After firsthand experience and implementation issues are resolved, dealers' opposition to the agency model may fade.
Strong intra-brand competition
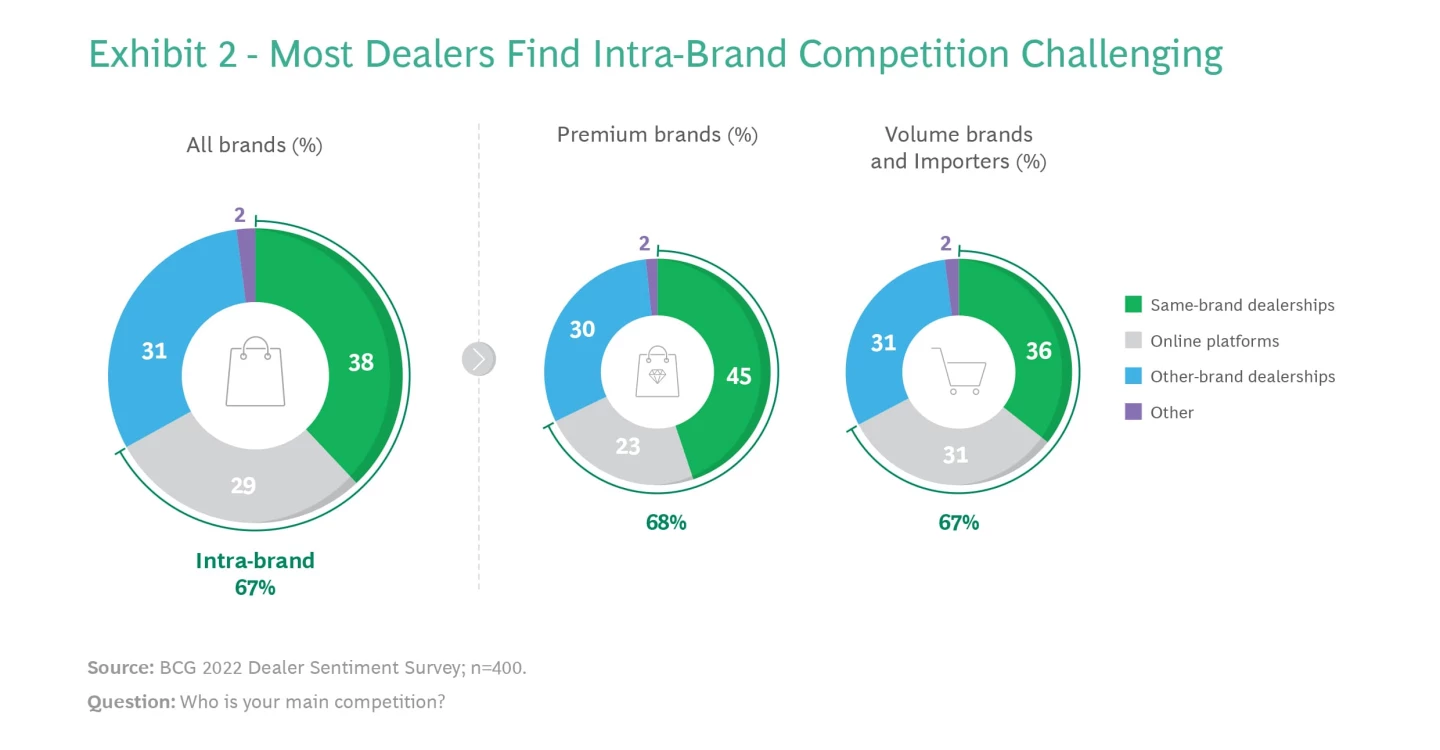
We shouldn't assume conventional dealers are happy with the status quo. Two-thirds said intra-brand dealers are their biggest rivals. See Exhibit 2. Brand A dealers would view another Brand A dealer across the city as a greater threat than a Brand B dealer next door.
In the traditional model, same-brand dealerships undercut each other to win loyal customers. Since dealerships can't capitalize on brand loyalty, they destroy each other's profit margins. This has caused dealerships to operate on razor-thin margins and prioritize cost-cutting measures like moving to rural areas over customer service.
We also found that independent platforms threaten volume and importer brands 31% more than premium-brand dealerships 23%. This is likely because volume buyers are more price-sensitive.
Implementing Automotive D2C Strategy
There are several direct-to-consumer automotive sales models. Online sales platforms for vehicle purchases could be created by manufacturers. One option is to open company-owned retail stores where customers can see vehicles and talk to representatives.
Many OEMs prefer a hybrid model where customers can buy cars online or at the dealership. The dealer takes customer orders, but the OEM fulfills them. Hybrid customers pay the OEM directly, not the dealer. The dealer's showroom will host vehicle test drives and product demos. The dealer will only stock demonstration vehicles, reducing infrastructure costs.
Tesla is perhaps the most famous automaker that sells directly to consumers. Tesla's stores and website allow customers to buy cars directly from the company. Other major US and European OEMs have tried D2C sales.
Technological Innovations Facilitating the Shift
Recent technological advances are helping the automotive industry move to online sales and DTC models:
- E-commerce and Digital Showrooms: Advanced online platforms let customers browse cars, customize them, and buy them.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: These technologies allow virtual car viewing and test drives, creating an immersive vehicle experience.
- Machine Learning and AI: These technologies make personalized recommendations based on consumer behavior.
For example, AI for car dealerships can be a powerful solution for cultivating lasting relationships by analyzing customer preferences, driving enhanced engagement, and driving success by converting internet leads into loyal customers.
- Financing and Digital Payment Solutions: Simplified financing and payment processes make online shopping easier.
Future Outlook
Online sales and DTC models will likely grow in automotive retail. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and virtual reality will improve digital car buying. The growing importance of cybersecurity and data privacy will also influence automakers' online sales strategies.
Automakers and bdc car dealership must be flexible and innovative to compete. Success in the changing automotive retail landscape requires digital transformation, new technology, and consumer preferences.
Conclusion
Finally, technology and consumer preferences are transforming the automotive retail industry. Online and direct-to-consumer (D2C) sales make vehicle sales more convenient and personalized. While traditional dealerships remain important, many OEMs are exploring hybrid models that combine online and offline channels.
Automakers can benefit from higher margins and direct customer relationships, while dealers worry about compensation, pricing dynamics, and business impact. With more dealers adopting digital-first sales models, opposition to new sales models may decrease.
Virtual reality, AI, and digital payment solutions will make online car buying more immersive and user-friendly. Leveraging these technologies, being flexible, and prioritizing customer satisfaction will help you succeed in this changing landscape and meet today's consumers' needs by blending digital and physical interactions.